Eons are geological time units that span millions to billions of years. They describe the Earth’s history, including its formation, evolution, and major events such as mass extinctions. But how long is an eon exactly? In this article, we will explore the definition of an eon, its subdivisions, and the key events that occurred in each eon.
What Is An Eon?
An eon is the largest geological time unit used to describe the Earth’s history. It is a period that lasts millions to billions of years, and it is characterized by significant changes in the Earth’s geology, climate, and biological diversity. The term “eon” was first introduced by the geologist John Phillips in 1841, and it is derived from the Greek word “aion,” which means age.
The Three Eons Of The Earth’s History
The Earth’s history is divided into three eons: the Archean Eon, the Proterozoic Eon, and the Phanerozoic Eon.
Archean Eon
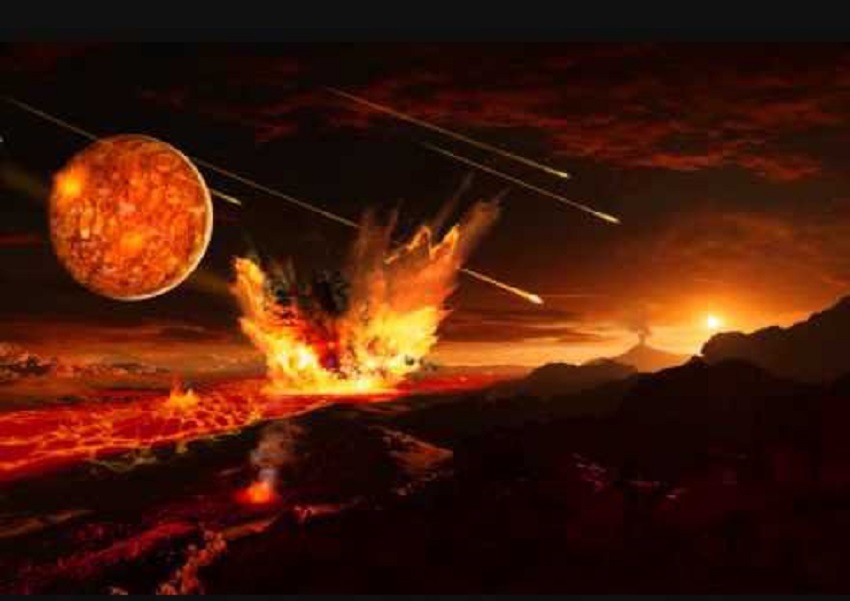
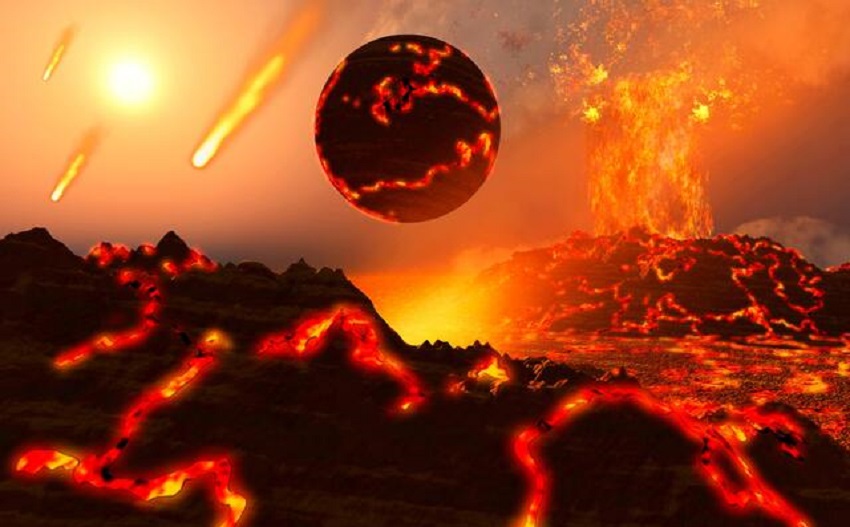
The Archean Eon is the oldest eon, lasting from around 4 billion years to 2.5 billion years ago. During this eon, the Earth’s surface was dominated by volcanic activity, and the atmosphere lacked oxygen. However, simple life forms, such as bacteria and blue-green algae, began to appear in the oceans.
Proterozoic Eon
The Proterozoic Eon lasted from 2.5 billion years ago to 542 million years ago. During this eon, the Earth’s atmosphere became oxygenated, which led to the evolution of more complex life forms, such as animals and plants. The first multicellular organisms appeared in the oceans, and the continents began to take their modern form.
Phanerozoic Eon
The Phanerozoic Eon began 542 million years ago and continues to the present day. The emergence of diverse life forms, such as mammals, birds, and reptiles characterizes it. The Earth’s climate also experienced significant changes, including ice ages and warm periods. Humans appeared during the most recent epoch of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is called the Holocene epoch.
Subdivisions Of The Eons
Each eon is divided into smaller units called eras, periods, and epochs. These subdivisions are based on significant geological and biological events during the eon. The following are the subdivisions of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is the most recent eon:
Paleozoic Era
The Paleozoic Era lasted from 542 million to 251 million years ago. The emergence of complex life forms, such as fish, amphibians, and reptiles characterizes it. The first land plants and insects also appeared during this era. The Paleozoic Era ended with the largest mass extinction event in the Earth’s history, which wiped out around 90% of all marine species.
Mesozoic Era
The Mesozoic Era lasted from 251 to 66 million years ago. It is commonly known as the “Age of Dinosaurs,” as many well-known dinosaur species lived during this era. The Mesozoic Era also saw the emergence of mammals, birds, and flowering plants. It ended with another mass extinction event, which wiped out the dinosaurs and many other species.
Cenozoic Era
The Cenozoic Era began 66 million years ago and continues today. The diversification of mammals, including the emergence of primates and humans characterizes it. The Earth’s climate also underwent significant changes, including the formation of ice sheets in Antarctica and several ice ages.
Conclusion
Eons are the largest geological time units used to describe the Earth’s history. They can last millions to billions of years and are characterized by significant changes in the Earth’s geology, climate, and biological diversity. The Earth’s history is divided into three eons: the Archean Eon, the Proterozoic Eon, and the Phanerozoic Eon. Each eon is divided into smaller units called eras, periods, and epochs. By understanding the different eons and their subdivisions, we can better appreciate the Earth’s long and complex history.